Published On Mar 31, 2021
.
Chapters
0:00 Introduction
1:02 Causes of Carotid artery disease
2:14 Symptoms of Carotid artery disease
2:47 Diagnosis of Carotid artery disease
3:30 Treatment of Carotid artery disease
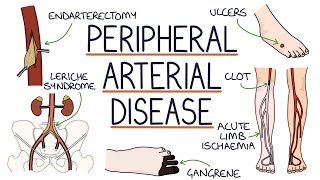
Carotid artery disease is a disease characterized by the buildup of a fatty or waxy substance called plaque inside the carotid arteries.
• The carotid arteries are two large blood vessels located on each side of the neck right below the angle of the jaw line. They each divide into the internal and external carotid arteries
• The internal carotid artery supply oxygenated blood to the front part of the brain where thinking, personality, and sensory-motor functions exist.
• The external carotid artery supply oxygenated blood to the face, scalp, and neck.
• In carotid artery disease, these arteries become narrowed or blocked as a result of the buildup of plagues.
• This, in turn, may block the blood flow to the brain, leading to TIA (transient ischemic attack) – a temporary shortage of blood to the brain and increasing the risk of stroke.
• Carotid artery disease is a very serious condition.
CAUSES
Carotid artery disease is caused by atherosclerosis, a condition in which plaque builds up in the arteries.
These plaques are made up of clumps of cholesterol, calcium, fibrous tissues and other cellular waste that gathers at microscopic injury site in the lining of the artery wall.
Atherosclerosis can make the carotid arteries stiff and narrow, limiting the amount of oxygen and nutrient delivered to vital brain structures that help with our day to day activities.
A further narrowing of the artery over time may cause the plaque to rupture, causing blood clots to form. A large blood clot may completely block the artery or small clots and plaques may travel up to the smaller arteries in the brain causing disruption of blood supply to parts of the brain.
Certain factors that may increase the risk of carotid artery disease are:
• Smoking
• High blood pressure
• High cholesterol
• Age
• Obesity
• Sedentary lifestyle
• A family history of atherosclerosis
• Sleep apnea
• Diabetes
• Insulin resistance.